CAN I REVERSE DIABETIC?
While diabetes cannot be "reversed" in the sense of completely curing the condition, it can often be managed effectively through lifestyle changes, medications, and sometimes surgical interventions. The goal of managing diabetes is to control blood sugar levels within a healthy range to prevent complications and improve overall health.
Here are some strategies that can help manage diabetes effectively:
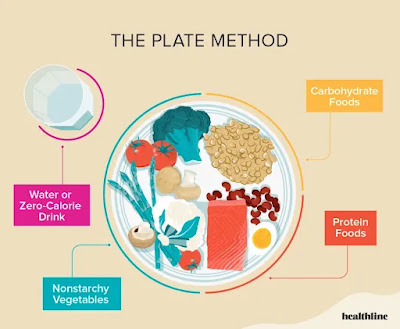
Healthy Eating: Following a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help regulate blood sugar levels. Portion control and carbohydrate counting may also be beneficial.
Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in regular exercise, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, can help improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week, along with strength training exercises.
Weight Management: Losing excess weight, if overweight or obese, can improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control. Even modest weight loss can have significant benefits for individuals with diabetes.
Medications: Some people with diabetes may require medications to help manage blood sugar levels. These may include oral medications such as metformin or sulfonylureas, injectable medications like insulin, or other types of drugs that help regulate blood sugar.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels: Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels can provide valuable information about how well diabetes is being managed and help identify trends or patterns that may require adjustments to treatment.
Stress Management: Stress can affect blood sugar levels, so finding ways to manage stress effectively, such as through relaxation techniques, mindfulness practices, or hobbies, can be beneficial.
Regular Medical Check-Ups: Regular visits to healthcare providers are important for monitoring diabetes control, assessing for complications, and adjusting treatment as needed.
It's important to note that the effectiveness of these strategies can vary depending on individual factors such as age, overall health, duration of diabetes, and genetic predisposition. Additionally, while these measures can help manage diabetes and improve quality of life, they may not completely eliminate the need for medications or insulin in some cases.
Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance on managing diabetes effectively. They can help develop a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to individual needs and circumstances.
Losing weight can play a significant role in managing and improving diabetes because excess body weight, particularly around the abdomen, can increase insulin resistance and make it harder for the body to regulate blood sugar levels effectively. Here's how weight loss can help better manage and sometimes even reverse diabetes: Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Losing weight, especially visceral fat (fat stored around the abdomen), can increase the body's sensitivity to insulin. This means that cells are better able to respond to insulin and take up glucose from the bloodstream, leading to better blood sugar control. Lowered Blood Sugar Levels: As insulin sensitivity improves, blood sugar levels tend to decrease. This can reduce the need for diabetes medications or insulin injections in some cases, or it may allow for lower doses to be used. Reduced Risk of Complications: Better blood sugar control resulting from weight loss can lower the risk of diabetes-related complications such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, nerve damage, and vision problems. Improved Cardiovascular Health: Losing weight can lead to improvements in blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and overall cardiovascular health, which are important considerations for individuals with diabetes who are at higher risk of heart disease. Increased Energy Levels: Achieving a healthier weight can lead to increased energy levels and overall well-being, making it easier to engage in regular physical activity and maintain other healthy habits that support diabetes management. Potential for Diabetes Remission: In some cases, significant weight loss achieved through lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise can lead to diabetes remission, where blood sugar levels return to normal without the need for diabetes medications. This is more likely to occur in individuals with type 2 diabetes who lose a substantial amount of weight shortly after diagnosis. It's important to note that while weight loss can have significant benefits for individuals with diabetes, it may not always lead to complete reversal of the condition, especially in cases of type 1 diabetes or long-standing type 2 diabetes. Additionally, weight loss should be achieved gradually through sustainable lifestyle changes rather than rapid or extreme measures, as crash diets or excessive weight loss can be harmful and may not lead to long-term success. Consulting with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian can help develop a personalized weight loss plan that is safe and effective for managing diabetes. adopting a high-protein, low-carbohydrate diet and eating smaller, more frequent meals can be beneficial for both weight control and diabetes management. Here's how each component can contribute: High-Protein, Low-Carbohydrate Diet: Protein: Foods high in protein can help promote satiety and reduce appetite, making it easier to control calorie intake and manage weight. Additionally, protein has a minimal impact on blood sugar levels compared to carbohydrates. Low Carbohydrates: Restricting carbohydrate intake can help stabilize blood sugar levels and reduce insulin resistance, which is beneficial for individuals with diabetes. By limiting carbohydrates, particularly refined carbohydrates and sugars, you can avoid spikes in blood glucose levels after meals. Small, Frequent Meals: Blood Sugar Control: Eating smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day can help prevent large fluctuations in blood sugar levels. This approach can help maintain more stable energy levels and avoid the sharp spikes and drops in blood glucose that can occur with large meals or long periods between meals. Appetite Regulation: Eating smaller meals more frequently can help regulate appetite and prevent overeating. This can be particularly beneficial for weight management, as it can help control calorie intake and promote a feeling of fullness. It's important to note that while a high-protein, low-carbohydrate diet and eating smaller meals can be effective strategies for weight control and diabetes management, individual dietary needs and preferences can vary. It's essential to work with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian to develop a personalized meal plan that takes into account factors such as medical history, medication use, lifestyle, and cultural preferences. Additionally, focusing on whole, nutrient-dense foods and incorporating a variety of food groups is key to achieving overall health and well-being.
Losing weight can play a significant role in managing and improving diabetes because excess body weight, particularly around the abdomen, can increase insulin resistance and make it harder for the body to regulate blood sugar levels effectively. Here's how weight loss can help better manage and sometimes even reverse diabetes: Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Losing weight, especially visceral fat (fat stored around the abdomen), can increase the body's sensitivity to insulin. This means that cells are better able to respond to insulin and take up glucose from the bloodstream, leading to better blood sugar control. Lowered Blood Sugar Levels: As insulin sensitivity improves, blood sugar levels tend to decrease. This can reduce the need for diabetes medications or insulin injections in some cases, or it may allow for lower doses to be used. Reduced Risk of Complications: Better blood sugar control resulting from weight loss can lower the risk of diabetes-related complications such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, nerve damage, and vision problems. Improved Cardiovascular Health: Losing weight can lead to improvements in blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and overall cardiovascular health, which are important considerations for individuals with diabetes who are at higher risk of heart disease. Increased Energy Levels: Achieving a healthier weight can lead to increased energy levels and overall well-being, making it easier to engage in regular physical activity and maintain other healthy habits that support diabetes management. Potential for Diabetes Remission: In some cases, significant weight loss achieved through lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise can lead to diabetes remission, where blood sugar levels return to normal without the need for diabetes medications. This is more likely to occur in individuals with type 2 diabetes who lose a substantial amount of weight shortly after diagnosis. It's important to note that while weight loss can have significant benefits for individuals with diabetes, it may not always lead to complete reversal of the condition, especially in cases of type 1 diabetes or long-standing type 2 diabetes. Additionally, weight loss should be achieved gradually through sustainable lifestyle changes rather than rapid or extreme measures, as crash diets or excessive weight loss can be harmful and may not lead to long-term success. Consulting with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian can help develop a personalized weight loss plan that is safe and effective for managing diabetes. adopting a high-protein, low-carbohydrate diet and eating smaller, more frequent meals can be beneficial for both weight control and diabetes management. Here's how each component can contribute: High-Protein, Low-Carbohydrate Diet: Protein: Foods high in protein can help promote satiety and reduce appetite, making it easier to control calorie intake and manage weight. Additionally, protein has a minimal impact on blood sugar levels compared to carbohydrates. Low Carbohydrates: Restricting carbohydrate intake can help stabilize blood sugar levels and reduce insulin resistance, which is beneficial for individuals with diabetes. By limiting carbohydrates, particularly refined carbohydrates and sugars, you can avoid spikes in blood glucose levels after meals. Small, Frequent Meals: Blood Sugar Control: Eating smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day can help prevent large fluctuations in blood sugar levels. This approach can help maintain more stable energy levels and avoid the sharp spikes and drops in blood glucose that can occur with large meals or long periods between meals. Appetite Regulation: Eating smaller meals more frequently can help regulate appetite and prevent overeating. This can be particularly beneficial for weight management, as it can help control calorie intake and promote a feeling of fullness. It's important to note that while a high-protein, low-carbohydrate diet and eating smaller meals can be effective strategies for weight control and diabetes management, individual dietary needs and preferences can vary. It's essential to work with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian to develop a personalized meal plan that takes into account factors such as medical history, medication use, lifestyle, and cultural preferences. Additionally, focusing on whole, nutrient-dense foods and incorporating a variety of food groups is key to achieving overall health and well-being.






















Comments